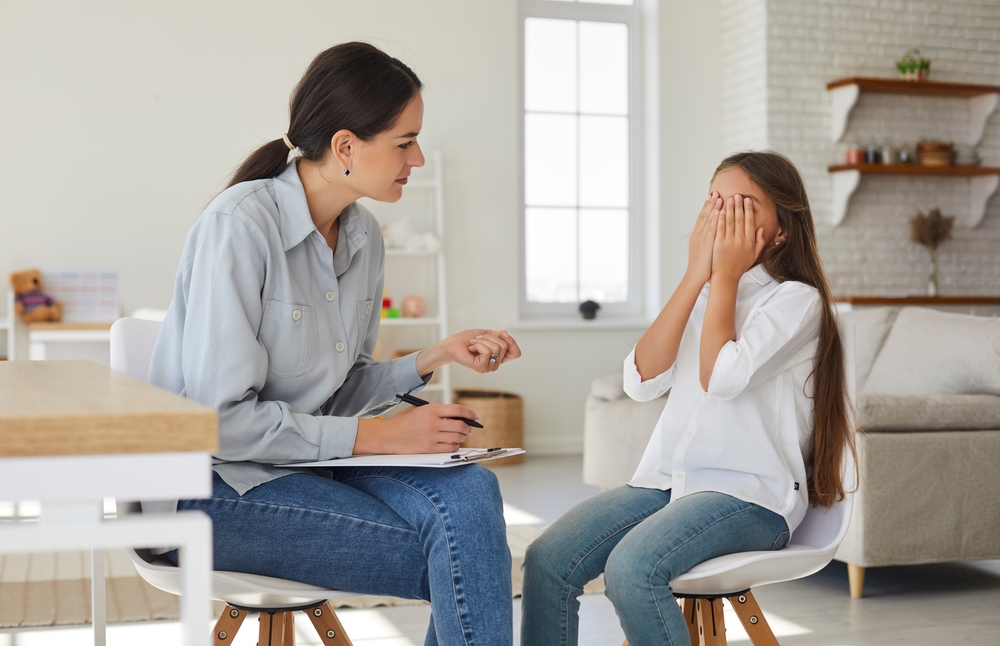
Anxiety is defined as “a feeling of worry, nervousness, or unease, typically about an imminent event or something with an uncertain outcome.” It is the body’s natural response to stress and will manifest differently in everyone. While fleeting anxiety is unavoidable, it is not healthy for a child to experience persistent and debilitating symptoms of anxiety. An adolescent may be struggling with an anxiety disorder when pervasive anxiety interferes with his or her ability to function in daily life.
There are many different therapeutic modalities that can be used to treat children with anxiety. With the help of a qualified mental health professional, the nuanced mental health needs of each adolescent will be considered and used to develop a customized treatment plan.
The specific components of a child’s anxiety treatment plan could consist of a combination of different therapeutic approaches. Nonetheless, cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is recognized as the first-line treatment for anxiety and is considered to be most effective form of psychotherapy for children with anxiety disorders, according to the Mayo Clinic.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
Cognitive behavioral therapy was developed in the 1960s by psychiatrist, Aaron Beck. It is a structured, short-term form of psychotherapy. CBT is based on the notion that one’s thoughts govern one’s feelings, which are directly linked to and influence one’s behaviors. Cognitive behavioral therapy relies on a goal-oriented approach to hone healthy coping mechanisms for reducing anxiety and toxic stress. In CBT, a therapist will encourage his or her client to discuss his or her troubling thoughts and/ or feelings. The steps of CBT include the following, provided by Psychology Today:
- Identify troubling situations and/ or conditions in your life.
- Become aware of your emotions, thoughts, and beliefs connected to these troubling situations and/ or conditions.
- Identify inaccurate and/ or negative thinking that may be contributing to your troubles.
- Reshape inaccurate and/ or negative thinking. To help facilitate this step, a therapist may encourage a child to consider whether their view of the situation and/ or condition is based off an inaccurate perception of the situation or off facts.
The way CBT works is that through therapy, a young person will learn to understand that the way they behave has a direct correlation with their personal attitudes and emotional problems. Through addressing and actively working on adapting unhelpful and inaccurate thoughts and feelings, a child can learn to replace these damaging thought processes with healthier behaviors and more positive emotions, which can help them prevent, reduce, manage, and even become more resilient towards anxiety.
Further Information and Support
For most of us, life can be very stressful, leading us to feel emotionally charged, which can cause anxiety, panic attacks, depression, and getting stuck in a cycle of being burdened with negative thoughts. Navigating through the challenges and emotional turmoil of life can be overwhelming, but you do not have to go through it alone. Engage Treatment is a Joint Commission Accredited professional psychological practice. We specialize in treating children, teens, and young adults struggling with depression and anxiety through community-focused treatment plans that incorporate a carefully selected combination of therapeutic interventions. Our compassionate, multidisciplinary practitioners are devoted to providing the highest quality of care that helps ignite positive change and enables clients to reach optimal health and well-being. Please do not hesitate to reach out for guidance. We are happy to answer questions and provide you with any additional information. Feel free to call us at 805-497-0605 or email us at [email protected]. You are also welcomed to get in touch by filling out our contact form. We look forward to connecting and having the opportunity to discuss how we might best be able to support you.
Contact Us
Westlake Campus:
IOP Program
2625 Townsgate Road, Suite 210
Westlake Village, California 91361
Agoura Campus:
Private Therapy & Parenting Program
30300 Agoura Road, Suite 250
Agoura Hills, CA 91301
805-497-0605
805-371-4862










© 2023 Engage Treatment Program, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
LGBTQ Friendly
About
• About Engage
• Our Team
• Career Opportunities
• Individual / Family Therapy






